Progress Bars
Progress
bars are used to show the
status of
an
operation. They are pretty easy to use, as you will see with the code
below. But first lets start out with the constructors that create a new
progress bar.
ProgressBar();
ProgressBar(Gtk::ProgressBarOrientation orientation);
ProgressBar(Gtk::ProgressBarOrientation orientation);
- PROGRESS_LEFT_TO_RIGHT (the default)
- PROGRESS_RIGHT_TO_LEFT
- PROGRESS_BOTTOM_TO_TOP
- PROGRESS_TOP_TO_BOTTOM
void
set_orientation(Gtk::ProgressBarOrientation orientation);void
set_fraction(double fraction);The 'fraction' argument is the amount completed, meaning the amount the progress bar has been filled from 0-100%. This is passed to the method as a real number ranging from 0 to 1.
As well as indicating the amount of progress that has occurred, the progress bar may be set to just indicate that there is some activity. This can be useful in situations where progress cannot be measured against a value range. The following method indicates that some progress has been made.
void
pulse();The step size of the activity indicator is set using the following method:
void
set_pulse_step(double fraction);When not in activity mode, the progress bar can also display a configurable text string within its trough, using the following method:
void
set_text(const String& text);You can turn off the display of the string by calling Gtk::ProgessBar::set_text() again with null as the argument.
The current text setting of a progress bar can be retrieved with the following method:
String
get_text() const;Progress Bars are usually used with timeouts or other such functions to give the illusion of multitasking. All will employ the Gtk::ProgressBar set_fraction() or pulse() methods in the same manner.
ProgessBar Example
Here is an example of a progress bar updated using timeouts. This code also shows you how to reset the progress bar.The header file for the ProgressBar example is <progressbar.hh>:
#include
<xfc/main.hh>
#include <xfc/gtk/progressbar.hh>
#include <xfc/gtk/window.hh>
using namespace Xfc;
class ProgressBarWindow : public Gtk::Window
{
Gtk::ProgressBar *progress_bar;
bool activity_mode;
sigc::connection timeout_connection;
protected:
bool on_timeout();
void
on_toggle_show_text();
void
on_toggle_activity_mode();
void
on_toggle_orientation();
public:
ProgressBarWindow();
~ProgressBarWindow();
};and the source file is <progressbar.cc>:
#include
"progressbar.hh"
#include <xfc/gtk/alignment.hh>
#include <xfc/gtk/box.hh>
#include <xfc/gtk/checkbutton.hh>
#include <xfc/gtk/separator.hh>
#include <xfc/gtk/table.hh>
#include <xfc/glib/main.hh>
ProgressBarWindow::ProgressBarWindow()
: activity_mode(false)
{
set_resizable(true);
set_title("ProgressBar Example");
set_border_width(0);
Gtk::VBox *vbox = new
Gtk::VBox(false, 5);
vbox->set_border_width(10);
add(*vbox);
vbox->show();
// Create a
centering
alignment object
Gtk::Alignment *align = new
Gtk::Alignment(0.5, 0.5);
vbox->pack_start(*align,
false,false, 5);
align->show();
// Create the
GtkProgressBar
progress_bar = new
Gtk::ProgressBar;
align->add(*progress_bar);
progress_bar->show();
// Add a timer callback to
update the value of the progress bar
timeout_connection =
G::timeout_signal.connect(sigc::mem_fun(this,
&ProgressBarWindow::on_timeout), 100);
Gtk::HSeparator *separator = new
Gtk::HSeparator;
vbox->pack_start(*separator,
false, false);
separator->show();
// Add table:
rows,
columns, homogeneous = false (by default)
Gtk::Table *table = new Gtk::Table(2, 2);
vbox->pack_start(*table, false);
table->show();
// Add a check
button to
select displaying of the trough text
Gtk::CheckButton *check = new
Gtk::CheckButton("Show
text");
table->attach(*check, 0, 1, 0, 1,
Gtk::EXPAND |
Gtk::FILL, Gtk::EXPAND | Gtk::FILL, 5, 5);
check->signal_clicked().connect(sigc::mem_fun(this,
&ProgressBarWindow::on_toggle_show_text));
check->show();
// Add a check
button to
toggle activity mode
check = new
Gtk::CheckButton("Activity mode");
table->attach(*check, 0, 1, 1, 2,
Gtk::EXPAND |
Gtk::FILL, Gtk::EXPAND | Gtk::FILL, 5, 5);
check->signal_clicked().connect(sigc::mem_fun(this,
&ProgressBarWindow::on_toggle_activity_mode));
check->show();
// Add a check
button to
toggle orientation
check = new
Gtk::CheckButton("Right to Left");
table->attach(*check, 0, 1, 2, 3,
Gtk::EXPAND |
Gtk::FILL, Gtk::EXPAND | Gtk::FILL, 5, 5);
check->signal_clicked().connect(sigc::mem_fun(this,
&ProgressBarWindow::on_toggle_orientation));
check->show();
// Add a button to
exit
the program
Gtk::Button *button = new
Gtk::Button("close");
button->signal_clicked().connect(sigc::mem_fun(this,
&ProgressBarWindow::dispose));
vbox->pack_start(*button, false,
false);
// This makes it
so the
button is the default.
button->set_flags(Gtk::CAN_DEFAULT);
// This grabs this
button to be the default button. Simply hitting the "Enter" key
// will cause this button to activate.
button->grab_default();
button->show();
}
ProgressBarWindow::~ProgressBarWindow()
{
timeout_connection.disconnect();
}
bool
ProgressBarWindow::on_timeout()
{
if
(activity_mode)
progress_bar->pulse();
else
{
//
Calculate the value of the progress bar using the value range set in
the
adjustment object
double
new_value = progress_bar->get_fraction() + 0.01;
if
(new_value > 1.0)
new_value =
0.0;
// Set
the
new value
progress_bar->set_fraction(new_value);
}
// As this is a timeout slot,
return true so that it continues to get called
return true;
}
void
ProgressBarWindow::on_toggle_show_text()
{
// Toggles the text display
within the progress bar trough
String text =
progress_bar->get_text();
if (!text.empty())
progress_bar->set_text("");
else
progress_bar->set_text("some
text");
}
void
ProgressBarWindow::on_toggle_activity_mode()
{
// Toggles the activity mode
of the progress bar
activity_mode = !activity_mode;
if (activity_mode)
progress_bar->pulse();
else
progress_bar->set_fraction(0.0);
}
void
ProgressBarWindow::on_toggle_orientation()
{
// Toggles the orientation of
the progress bar
if
(progress_bar->get_orientation() == Gtk::PROGRESS_LEFT_TO_RIGHT)
progress_bar->set_orientation(Gtk::PROGRESS_RIGHT_TO_LEFT);
else
progress_bar->set_orientation(Gtk::PROGRESS_LEFT_TO_RIGHT);
}
int main (int
argc, char *argv[])
{
using namespace Main;
init(&argc, &argv);
ProgressBarWindow window;
window.signal_destroy().connect(sigc::ptr_fun(&Xfc::Main::quit));
window.show();
run();
return 0;
}Compiling ProgressBar
If you compiled and installed XFC yourself, you will find the source
code for ProgressBar in the
<examples/progressbar> source directory along with a Makefile. If
XFC came pre-installed, or you installed it from an RPM package, you
will
find the source code in the
</usr/share/doc/xfcui-X.X/examples/progressbar> subdirectory. In
this case you will have to create the Makefile yourself (replace X.X
with the
version number of the libXFCui library you have installed).To create a Makefile for ProgressBar, add the following lines to a new text file and save it using the name "Makefile":
CC = g++
CFLAGS = -Wall -O2
progressbar: progressbar.cc progressbar.hh
$(CC) progressbar.cc -o progressbar $(CFLAGS)
`pkg-config xfcui-X.X --cflags --libs`
clean:
rm -f *.o progressbarIf you cut and paste these lines make sure the whitespace before $(CC) and rm is a tab character. When you compile and run this program you will see the following window appear:
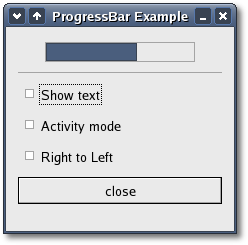
Checking the 'Show text' check button displays the text string 'some text' in the progress bar trough. Checking the right-to-left check button will make the progress bar update from the right side instead of the left. Checking the 'Activity mode' check button will switch the progess bar into action mode. In this mode the progess bar displays a block that moves up and down the trough at a constant rate to indicate that some activity is occuring.
| Copyright © 2004-2005 The XFC Development Team | Top |
XFC
4.4 |